Economic Value Definition Examples
Economic value refers to the worth or utility that a product or service provides to individuals or organizations. It is a measure of the benefit or satisfaction that can be derived from consuming or using a particular good or service.
There are various examples of economic value, including:
- Monetary Value: This is the most common form of economic value, which is expressed in terms of money. For example, the price of a product or service indicates its monetary value.
- Utility Value: This refers to the usefulness or satisfaction that a product or service provides to a consumer. For example, a smartphone has utility value because it allows individuals to communicate, access information, and perform various tasks.
- Emotional Value: Some products or services have emotional value, meaning they evoke positive emotions or fulfill emotional needs. For example, a luxury handbag may have emotional value for someone who values status or fashion.
- Environmental Value: Certain products or services have environmental value because they contribute to environmental sustainability or conservation. For example, renewable energy sources have environmental value because they reduce reliance on fossil fuels and decrease carbon emissions.
By recognizing the different examples of economic value, businesses can better meet the needs and desires of their target audience, ultimately leading to increased customer satisfaction and profitability.
Factors Affecting Economic Value
Several factors influence the economic value of a product or service:
- Scarcity: The rarer a product or service is, the higher its economic value. Scarcity creates a sense of exclusivity and increases demand.
- Demand and Supply: The relationship between demand and supply affects economic value. When demand exceeds supply, the economic value of a product or service increases.
- Utility: The usefulness or satisfaction that a product or service provides to consumers affects its economic value. Products or services that fulfill a specific need or solve a problem tend to have higher economic value.
- Competition: The level of competition in the market can impact the economic value of a product or service. In a highly competitive market, prices may be driven down, reducing the economic value.
- Perceived Quality: The perceived quality of a product or service influences its economic value. Higher quality products or services are often associated with higher economic value.
Measuring Economic Value
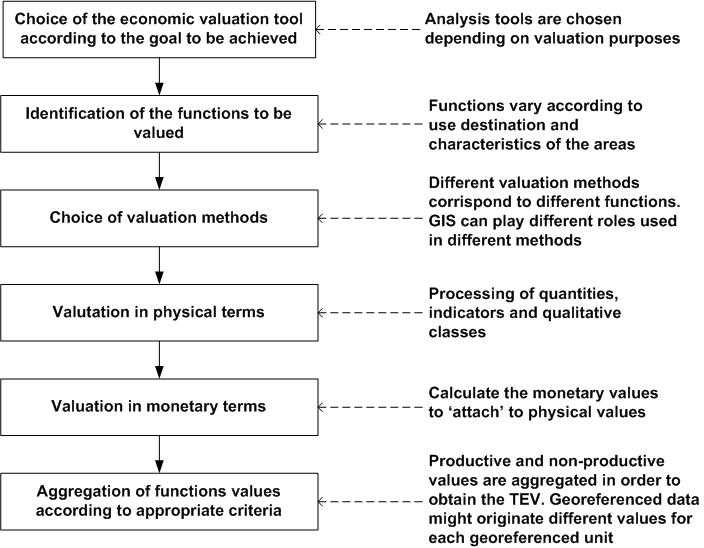
There are various methods to measure economic value, including:
- Market-based approach: This approach involves analyzing the prices of similar products or services in the market to estimate the economic value.
- Cost-based approach: This approach considers the cost of producing a product or service and adds a profit margin to determine its economic value.
- Value-based approach: This approach considers the overall value that a product or service provides to consumers, taking into account factors such as convenience, durability, and customer satisfaction.
Examples of Economic Value
Economic value refers to the worth or utility that a product or service provides to individuals or businesses. It is a measure of the benefits that can be derived from consuming or using a particular item. Here are some examples of economic value:
1. Cost savings
One way that economic value can be demonstrated is through cost savings. For example, if a company implements a new technology that reduces production costs, it can pass on those savings to customers in the form of lower prices. This provides economic value to customers who can now purchase the product at a lower cost.
2. Time savings
Another example of economic value is time savings. Time is a valuable resource, and any product or service that helps individuals or businesses save time can be considered to have economic value. For instance, a software program that automates repetitive tasks can save employees hours of work, allowing them to focus on more important tasks. This time savings translates into economic value for the company.
Products or services that increase productivity can also provide economic value. For example, a piece of machinery that allows a factory to produce more goods in less time can increase the company’s output and revenue. This increased productivity is a form of economic value as it helps the company generate more profits.
4. Improved quality
Improved quality is another way that economic value can be demonstrated. When a product or service offers better quality than its competitors, it provides additional value to customers. For instance, a smartphone with a high-resolution camera and advanced features may be more expensive than other models, but it offers superior quality and functionality. Customers who value these features are willing to pay a premium for the product, demonstrating the economic value it provides.
Ways to Estimate Economic Value
1. Market Research
Market research involves gathering data about consumer preferences, purchasing behavior, and market trends. By analyzing this data, businesses can gain insights into the economic value that consumers place on different products or services. Market research can be conducted through surveys, focus groups, or by analyzing existing data.
2. Comparative Analysis
Comparative analysis involves comparing the economic value of a product or service to similar offerings in the market. By examining the features, benefits, and pricing of competing products, businesses can determine how their offering stacks up and estimate its economic value relative to the competition.
3. Cost-Based Analysis
Cost-based analysis involves estimating economic value based on the cost of production or delivery. This method takes into account the expenses involved in creating or providing a product or service and calculates a price that covers these costs while still providing a profit. However, cost-based analysis may not fully capture the economic value perceived by consumers.
4. Conjoint Analysis
Conjoint analysis is a statistical technique that measures the economic value of different product attributes or features. By presenting consumers with different combinations of attributes and asking them to rank their preferences, businesses can estimate the economic value that consumers place on each attribute. This information can then be used to optimize product design and pricing.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
