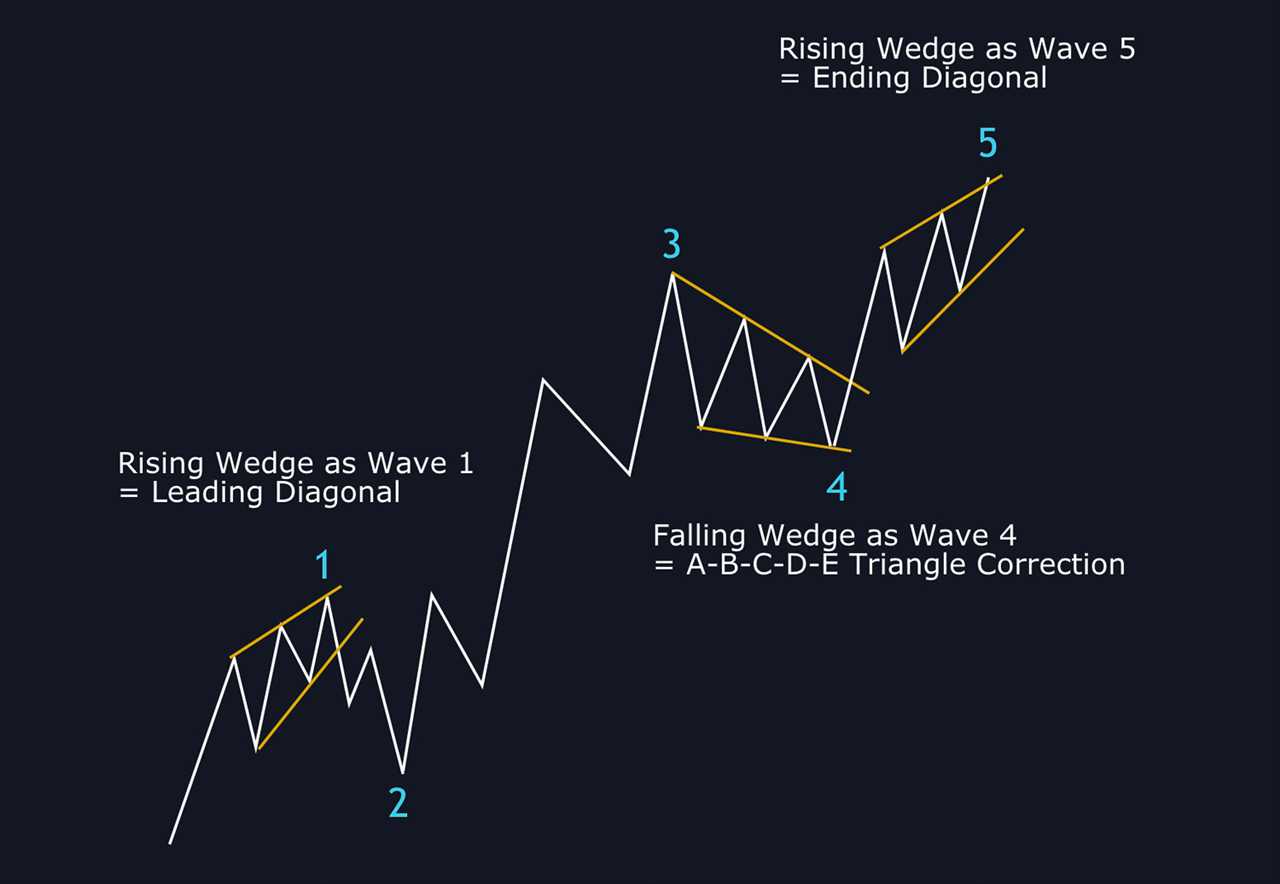
What Is a Wedge and What Are Falling and Rising Wedge Patterns?
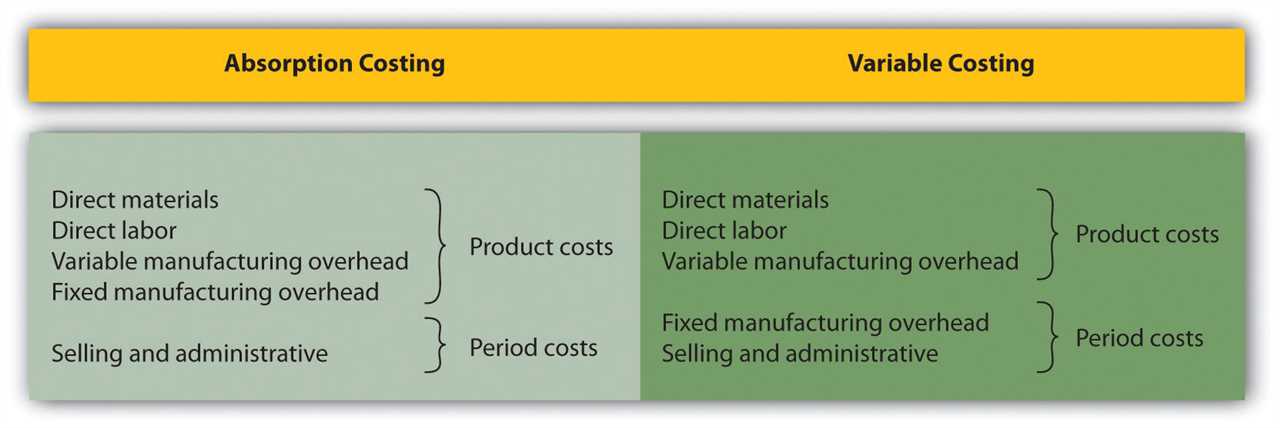
What Is a Wedge Pattern? A wedge pattern is a technical analysis pattern that is formed when the price of an asset consolidates between two converging trendlines. The trendlines can be either ascending (rising wedge) or descending (falling wedge). Traders and investors use the wedge pattern to identify potential trading … …